Use of Throw and Throws keywords in Java
- Keshari Abeysinghe

- Feb 24, 2020
- 2 min read
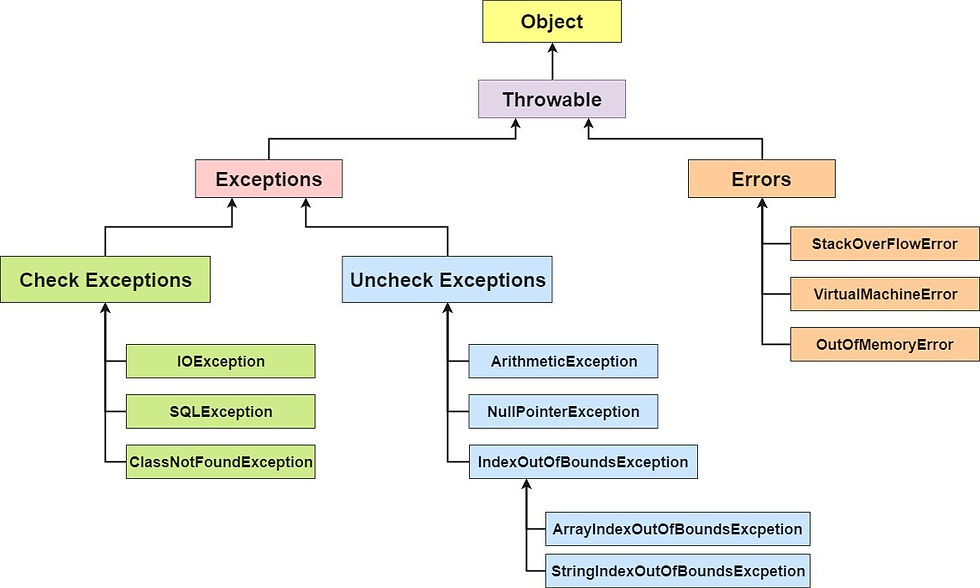
In Java we have already defined exception classes such as ArithmeticException, NullPointerException, ArrayIndexOutOfBounds exception etc. These exceptions are set to trigger on different-2 conditions.
We can define our own set of conditions or rules and throw an exception explicitly using throw keyword. For example, we can throw ArithmeticException when we divide number by 5, or any other numbers, what we need to do is just set the condition and throw any exception using throw keyword.
We can throw either checked or uncheked exception in java by throw keyword. The throw keyword is mainly used to throw custom exception. We will see custom exceptions later.
The syntax of java throw keyword is given below.
throw new exception_class("error message");throw new ArithmeticException("dividing a number by 5 is not allowed in this program");Example
public class Example1
{
static void validate(int age){
if(age<18)
throw new ArithmeticException("not valid");
else
System.out.println("welcome to vote");
}
public static void main(String args[]){
validate(13);
System.out.println("rest of the code...");
}
}
Expected Output
Exception in thread main java.lang.ArithmeticException:not validThrows Keyword
The throws keyword is used to declare the list of exception that a method may throw during execution of program. Any method that is capable of causing exceptions must list all the exceptions possible during its execution, so that anyone calling that method gets a prior knowledge about which exceptions are to be handled. A method can do so by using the throws keyword.
The syntax of java throws keyword is given below.
type method_name(parameter_list) throws exception_list
{
// definition of method
}
Example of Throws keyword
class Example2
{
static void check()
throws ArithmeticException
{
System.out.println("Inside check function");throw new
ArithmeticException("demo");
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
try{
{
check();
}
catch(ArithmeticException e){
{
System.out.println("caught" + e);
}
}
}
}
}
Expected Output
Inside check function
caughtjava.lang.ArithmeticException: demo

Happy Coding!
Comments