Nested Try-Catch block
- Keshari Abeysinghe

- Feb 25, 2020
- 1 min read
Updated: Jun 8, 2021
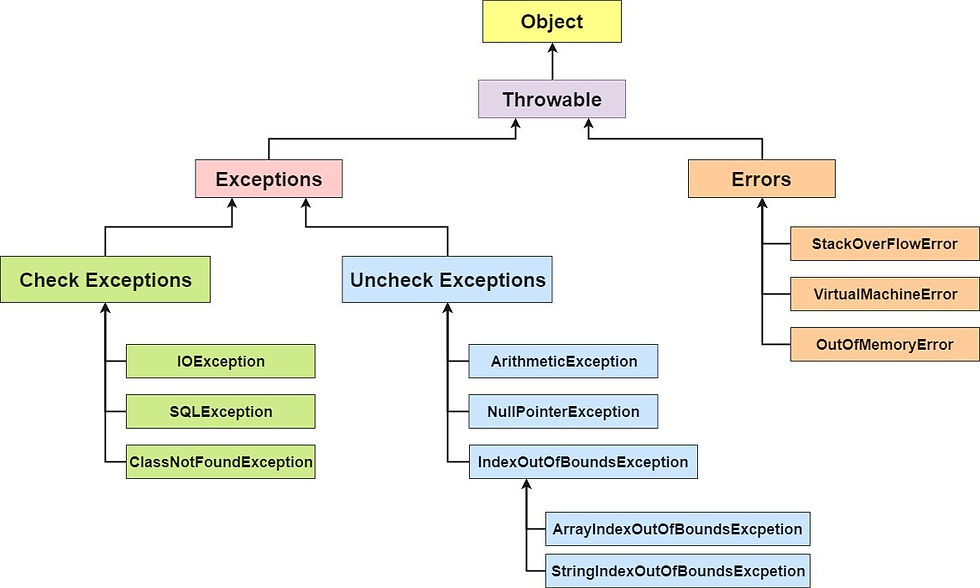
When a try catch block is present in another try block then it is called the nested try catch block.Sometimes a situation may arise where a part of a block may cause one error and the entire block itself may cause another error. In such cases, exception handlers have to be nested.
Let's see a simple example of java nested try block.
class Example1
{
public static void main(String args[]){
//main try-block
try{
//try-block2
try{
//try-block3
try{
int arr[]= {1,2,3,4};
/* I'm trying to display the value of
* an element which doesn't exist. The
* code should throw an exception
*/
System.out.println(arr[10]);
}catch(ArithmeticException e){
System.out.print("Arithmetic Exception");
System.out.println(" handled in try-block3");
}
}
catch(ArithmeticException e){
System.out.print("Arithmetic Exception");
System.out.println(" handled in try-block2");
}
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e4){
System.out.print("ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException");
System.out.println(" handled in main try-block");
}
}
} Expected Output
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException handled in main try-blockThis is how the structure is:
try-block3 is inside try-block2 and try-block2 is inside main try-block, you can say that the main try-block is a grand parent of the try-block3. Refer the explanation which is given at the end of this code.As you can see that the ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException occurred in the grand child try-block3. Since try-block3 is not handling this exception, the control then gets transferred to the parent try-block2 and looked for the catch handlers in try-block2. Since the try-block2 is also not handling that exception, the control gets transferred to the main (grand parent) try-block where it found the appropriate catch block for exception.
This is how the the nesting structure works.
Happy Coding!
Comments