Introduction to Threads in Java
- Keshari Abeysinghe

- Aug 3, 2020
- 2 min read
Updated: Dec 7, 2020
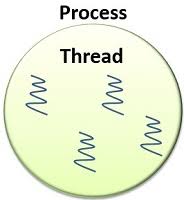
What is a thread ?
A thread is a lightweight sub-process, the smallest unit of processing.
Threads are independent. If there occurs an exception in one thread, it doesn't affect other threads.thread is executed inside the process.There can be multiple processes inside the OS, and one process can have multiple threads.Threads use a shared memory area. They don't allocate separate memory areas so saves memory, and context-switching between the threads takes less time than process.
What is MultiThreading
Multithreading in Java is a process of executing multiple threads simultaneously.It doesn't block the user because threads are independent and it doesn't affect other threads if an exception occurs in a single thread.As threads are used shared memory ,you can perform multiple operations at the same time.Java Multithreading is mostly used in games, animation, etc.
Advantage of Multi-threading
Multi-threading reduces the CPU idle time that increase overall performance of the system. Since thread is lightweight process then it takes less memory and perform context switching as well that helps to share the memory and reduce time of switching between threads.
Thread has many advantages over the process to perform multitasking. Process is heavy weight, takes more memory and occupy CPU for longer time that may lead to performance issue with the system. To overcome these issue process is broken into small unit of independent sub-process and called them as threads that can perform independent task efficiently. So nowadays computer systems prefer to use thread over the process and use multithreading to perform multitasking.
Threads execution follows following life cycle
Life cycle of the thread
1. New
Thread is in new state before the newly created thread class instance is invocate in to start () method.
2. Runnable
The thread is in runnable state after invocation of start() method, but the thread scheduler has not selected it to be the running thread.
3. Running
The thread is in running state if the thread scheduler has selected it.
4. Non-Runnable (Blocked)
This is the state when the thread is still alive, but is currently not eligible to run.
5. Terminated
The Thread which is dead or terminated before to run() method is exists .
Oops ! how to create a thread?
visit the next post Creating Threads .
Happy Coding !



Comments